Precision in a shot: transforming gold nanocubes into diagnostic-grade spheres
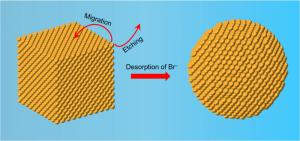
GA, UNITED STATES, June 16, 2025 /EINPresswire.com/ -- Gold nanospheres play a pivotal role in point-of-care diagnostics, but manufacturing them at scale with uniform size and shape has long posed a technical hurdle. A new study reports a simplified one-shot synthesis technique that overcomes this challenge by transforming gold nanocubes into consistently sized 35 nm nanospheres through heat-induced surface reactions. This approach bypasses the need for slow, dropwise precursor addition—long considered necessary for precision—using instead a high-temperature incubation process that triggers bromide ion desorption, oxidative etching, and atom migration. The result is a reproducible, scalable method that delivers high-quality nanospheres ideally suited for biomedical applications such as rapid pathogen detection.
Lateral flow immunoassays (LFIAs), best known for their use in home COVID-19 tests, rely heavily on the optical properties of gold nanoparticles to produce fast, visible results. However, traditional synthesis methods often yield particles with inconsistent morphology, compromising test accuracy. Uniform gold nanospheres larger than 30 nm are particularly desirable, as their sharp optical signals and large surface areas enhance both sensitivity and binding efficiency. But achieving this uniformity typically requires time-consuming dropwise chemical dosing, which complicates scale-up. Because of these limitations, there is a pressing need for a more efficient, controllable synthesis route to produce diagnostic-grade nanospheres at industrial scale.
In a study published March 29, 2025, in Precision Chemistry, researchers from the Georgia Institute of Technology introduced a novel one-shot precursor injection method to synthesize uniform 35 nm gold nanospheres—eliminating the traditional need for stepwise precursor addition. By leveraging elevated temperature and bromide ion chemistry, the team achieved a cube-to-sphere transformation process that yields particles with exceptional uniformity. The synthesized nanospheres rival or surpass those produced by slower, less scalable techniques, signaling a major step forward in nanomaterial manufacturing for next-generation diagnostic tools.
The synthesis strategy unfolds in three stages. First, small 10 nm gold spheres are formed via rapid one-shot precursor injection. These serve as seeds, which are then grown into 30 nm nanocubes using a single-step method involving potassium bromide to selectively cap certain crystal facets and control growth. In the final stage, the nanocubes undergo thermal incubation in a CTAC solution at 97°C. This triggers bromide desorption from the surface, setting off a dual mechanism of oxidative etching and surface atom migration, which reshapes the cubes into highly uniform spheres. Spectroscopic data confirmed a gradual blue-shift and narrowing of the plasmon resonance peak, signaling a successful transition to the desired spherical morphology. Comparative tests showed that these spheres exhibit better or equal uniformity, optical clarity, and colloidal stability than those produced by dropwise techniques. Moreover, the compatibility of this approach with continuous-flow systems highlights its potential for commercial-scale production without compromising quality or consistency.
This research was to streamline gold nanosphere synthesis while maintaining top-tier quality. And results show by unlocking the role of bromide in the shape transformation process, it was able to design a method that's not only scientifically elegant but also commercially practical. This one-shot approach connects fundamental nanochemistry with scalable engineering, making it possible to manufacture high-performance nanoparticles that meet real-world diagnostic needs.
The ability to mass-produce uniform gold nanospheres has wide-ranging implications, especially for medical diagnostics where speed, accuracy, and scalability are essential. These particles can be tailored with biomolecular coatings to detect specific pathogens with high precision, making them valuable in outbreak scenarios or remote healthcare settings. Beyond diagnostics, the method could also benefit fields like drug delivery, biosensing, and photothermal cancer therapy, where particle consistency directly influences effectiveness. As the demand for precision nanomaterials accelerates, this breakthrough offers a scalable, reproducible path to meet the growing needs of next-generation biomedical technologies.
References
DOI
10.1021/prechem.4c00105
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.1021/prechem.4c00105
Funding information
This work was supported in part by a sponsored project from the Gemina Laboratories for the synthesis, a research grant from the NSF (CHE-2002653) for the SERS measurements, and start-up funds from the Georgia Institute of Technology.
Lucy Wang
BioDesign Research
email us here
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.